High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a condition where the force of blood pushing against the artery walls is consistently too high. Often called the “silent killer,” it frequently has no noticeable symptoms, making regular monitoring essential. Anyone can develop hypertension, but certain groups are at higher risk, including older adults, individuals with a family history of hypertension, and those with unhealthy lifestyles. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent serious complications like heart attack, stroke, and kidney disease.
Causes & Risk Factors
Hypertension can be classified as primary (essential) or secondary. Primary hypertension, which accounts for most cases, has no identifiable cause but is influenced by genetic and lifestyle factors. Secondary hypertension is caused by an underlying medical condition, such as kidney disease, sleep apnoea, or thyroid problems. Major risk factors include a high-sodium diet, lack of physical activity, obesity, excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, and chronic stress.
Symptoms
Hypertension often has no symptoms, which is why regular blood pressure checks are vital. In severe cases, symptoms may include headaches, dizziness, nosebleeds, or shortness of breath. Mild to moderate hypertension usually presents without any noticeable signs. If you experience severe headaches, chest pain, or vision changes, seek immediate medical attention, as these could indicate a hypertensive crisis.
Diagnosis
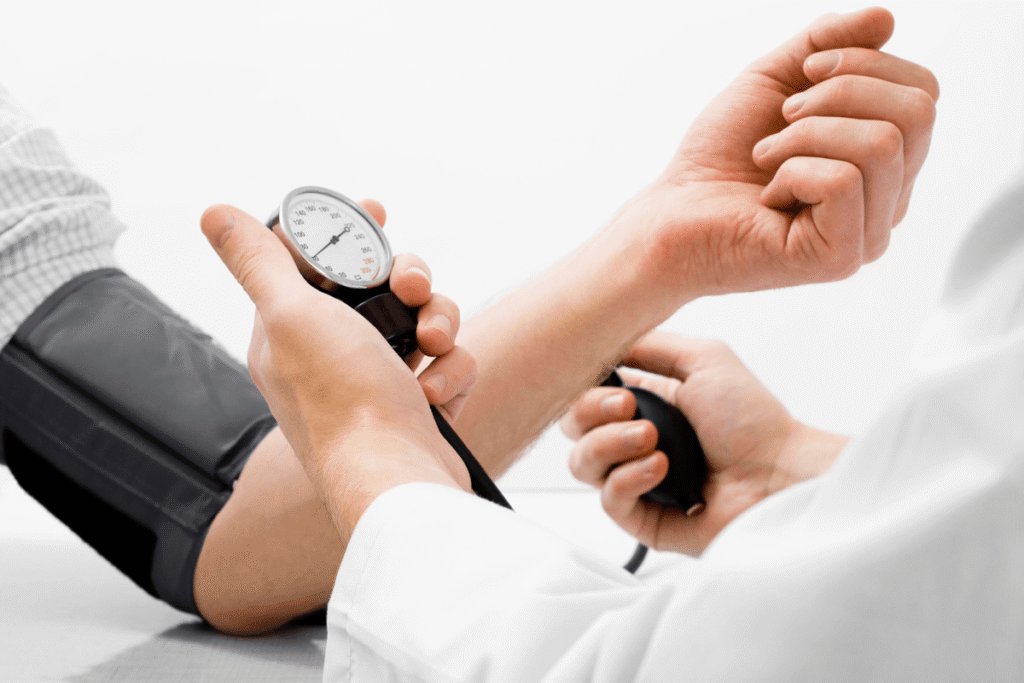
Diagnosing hypertension involves measuring blood pressure using a cuff and monitor. Regular blood pressure readings are taken over time to confirm the diagnosis. Additional tests may include blood tests to check cholesterol and kidney function, an electrocardiogram (ECG) to assess heart health, and a 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitor for more accurate readings. Early detection is vital to prevent long-term damage to the heart and blood vessels.
Treatment Options
Treatment for hypertension focuses on lowering blood pressure and reducing the risk of complications. Lifestyle changes are the first line of defence, including a low-sodium DASH diet, regular exercise, weight management, and smoking cessation. Medications like diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers are commonly prescribed to lower blood pressure. In some cases, a combination of medications may be necessary.
Complications & Risks
Untreated hypertension can lead to serious complications, including heart attack, stroke, kidney failure, and vision loss. The increased pressure can damage arteries, leading to atherosclerosis and organ damage. Chronic hypertension can significantly impact quality of life, increasing the risk of cognitive decline and other health problems.
Prevention & Management
Preventing hypertension involves adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle. This includes maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet low in sodium and saturated fats, exercising regularly, limiting alcohol consumption, and avoiding smoking. Regular blood pressure checks are crucial for monitoring and early detection. Managing stress and getting adequate sleep are also essential. Regular check-ups with your doctor are vital for monitoring blood pressure and adjusting treatment as needed.
If you have concerns about your blood pressure or risk factors for hypertension, it’s important to seek medical advice. Our experienced cardiologists can provide comprehensive evaluations, accurate diagnoses, and personalised treatment plans to help you manage your hypertension and improve your heart health. Don’t let high blood pressure silently damage your health. Schedule a consultation today and take control of your cardiovascular well-being.