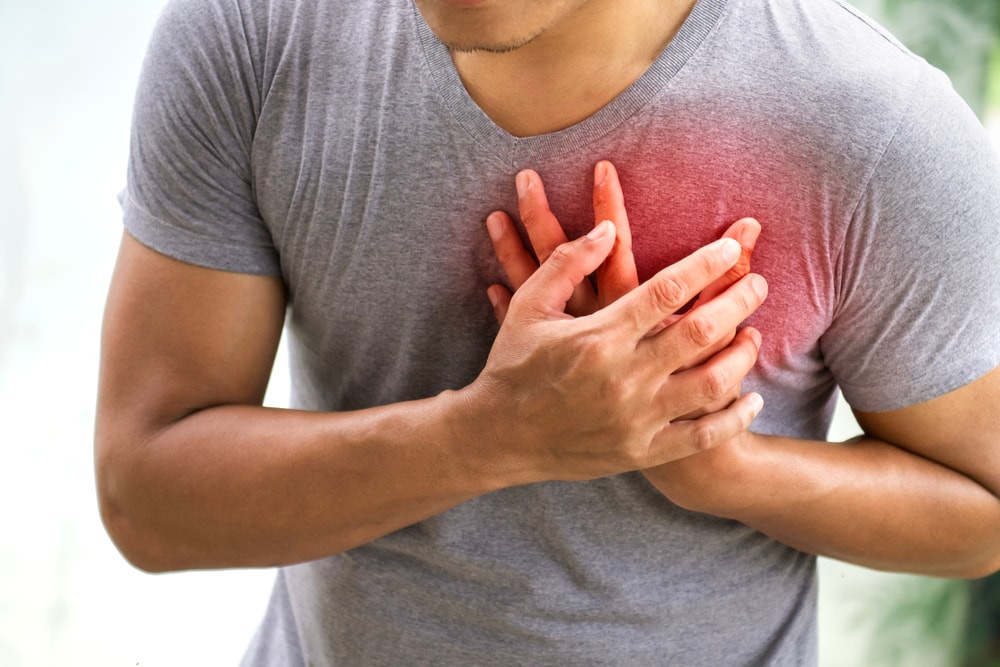
Angina, often described as chest pain or discomfort, is a signal from your heart that it’s not receiving enough oxygen-rich blood. It’s a symptom, not a disease itself, and it’s crucial to pay attention to it. Individuals at risk include those with a family history of heart disease, older adults, and those leading a sedentary lifestyle. Early diagnosis and treatment are vital to prevent serious cardiac events.
Causes & Risk Factors
The most common cause of angina is Coronary Artery Disease (CAD), where the arteries supplying blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked by plaque buildup. This can be influenced by genetics, but lifestyle factors play a significant role. Major risk factors include smoking, obesity, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, diabetes, and a lack of physical activity. Other medical conditions like anaemia can also contribute.
Symptoms
Angina symptoms can vary, but typically involve chest pain, tightness, pressure, or a squeezing sensation. This discomfort may radiate to the shoulders, arms, neck, jaw, or back. Mild angina might only occur during physical exertion, while severe angina can happen even at rest. If you experience sudden, intense chest pain, especially accompanied by shortness of breath, sweating, or nausea, seek immediate medical attention.
Diagnosis
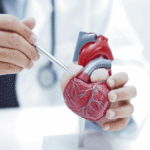
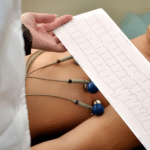
Diagnosing angina involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. An Electrocardiogram (ECG) can detect abnormalities in heart rhythm. Blood tests can assess cholesterol levels and other markers of heart health. Imaging tests like coronary angiography or CT Scans provide detailed images of the coronary arteries to identify blockages. Early detection is paramount to prevent further cardiac damage.
Treatment Options
Treatment for angina focuses on relieving symptoms and reducing the risk of future heart problems. Lifestyle changes are fundamental, including a heart-healthy diet low in saturated fats, regular exercise, and smoking cessation. Medications like nitrates, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers can help relax blood vessels and improve blood flow. In severe cases, procedures such as angioplasty (to widen narrowed arteries) or coronary artery bypass surgery may be necessary
Complications & Risks
Untreated angina can lead to serious complications, including heart attack and heart failure. Chronic angina can significantly impact quality of life, limiting physical activity and causing emotional distress. It’s essential to manage angina effectively to minimise these risks and maintain long-term heart health.
Prevention & Management
Preventing angina involves adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle. This includes maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking. Regular check-ups with your doctor are crucial for monitoring heart health and adjusting treatment as needed. Managing stress and controlling blood pressure and cholesterol levels are also vital.
Concerned about chest pain or heart health? We understand the fears that come with cardiac health. Our team of experienced cardiologists offers comprehensive assessments, personalised treatment plans, and ongoing support to help you manage angina and improve your quality of life. Don’t let chest pain dictate your life. Book a consultation today and take the first step towards a healthier heart.