Key takeaways:
- A 12-lead ECG is a simple, non-invasive test that records your heart’s electrical activity
- It helps detect arrhythmias, signs of past or current heart attacks, and other heart-related abnormalities
- The test can identify silent conditions even if you don’t feel symptoms
- Useful for both emergency evaluations and routine screenings
- Results help guide further cardiac investigations when needed
What Is a 12-Lead ECG?
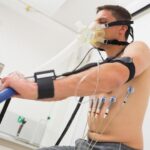
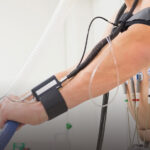
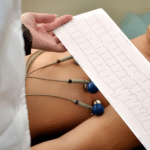
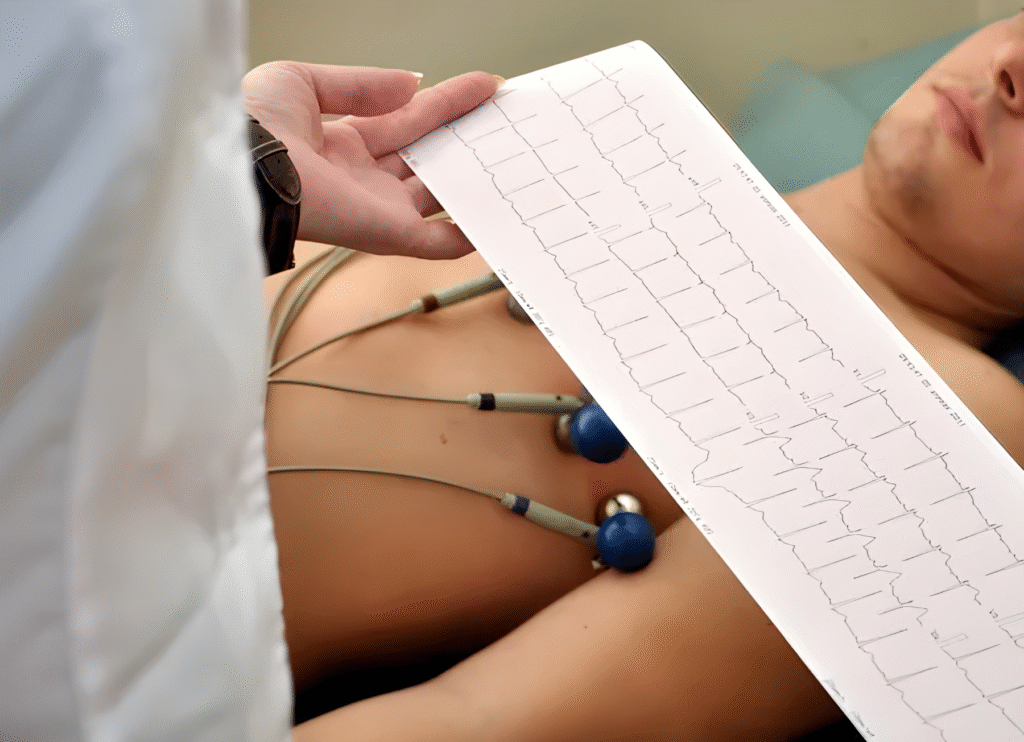
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a test that records the electrical signals produced by your heart as it beats. The “12-lead” refers to the twelve different angles or perspectives the machine uses to assess your heart’s activity, using electrodes placed on your chest, arms, and legs.
It is painless, quick, and commonly used to evaluate symptoms like chest discomfort, palpitations, breathlessness, dizziness, or even as part of a routine cardiac check.
7 Heart Conditions a 12-Lead ECG Can Help Detect
Even if you’re not feeling unwell, an ECG can uncover silent or hidden heart problems. Here’s what it can show:
1. Atrial Fibrillation and Other Arrhythmias
An ECG can detect irregular or abnormal heart rhythms, including:
- Atrial fibrillation (AF)
- Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)
- Premature beats (PVCs or PACs)
- Heart blocks (slow conduction)
These rhythm disturbances can cause palpitations, dizziness, or no symptoms at all—and some increase the risk of stroke or heart failure.
2. Signs of a Past Heart Attack (Old Infarct)
A 12-lead ECG may reveal changes in wave patterns that suggest a previous heart attack, one that may have gone unnoticed if symptoms were mild or mistaken for indigestion or fatigue. This is important for guiding follow-up care and risk assessment.
3. Current or Ongoing Ischemia (Reduced Blood Flow)
When blood flow to the heart muscle is reduced —as in angina or a developing heart attack— certain changes in the ECG (like ST depression or elevation) may appear. This makes the ECG a useful first test in the evaluation of chest pain.
4. Heart Blocks and Conduction Delays
Electrical signals in the heart can sometimes be delayed or blocked, resulting in a slower heart rate or missed beats.
An ECG can show patterns such as:
- First-degree, second-degree, or third-degree AV block
- Bundle branch block (e.g., left or right bundle branch block)
These findings help determine if further intervention is needed.
5. Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (Thickened Heart Muscle)
In people with longstanding high blood pressure or structural heart issues, the ECG may show signs of an enlarged or thickened heart muscle. While not a conclusive diagnosis, it prompts further testing like echocardiography.
6. Electrolyte Abnormalities
Low or high levels of potassium, calcium, or magnesium can affect how the heart beats. An ECG can reveal patterns that suggest these imbalances, often before symptoms become severe.
7. Pericarditis or Inflammation of the Heart Lining
Changes in multiple ECG leads may point to pericarditis, a condition where the sac surrounding the heart becomes inflamed. This can cause chest pain that’s different from angina.
When Should You Consider Getting an ECG?
An ECG may be recommended if you:
- Have symptoms like chest discomfort, palpitations, breathlessness, or fainting
- Have a personal or family history of heart disease
- Are undergoing pre-surgery screening
- Have high blood pressure, diabetes, or high cholesterol
- Are participating in sports screening
- Are starting certain medications that may affect the heart rhythm
5 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Is an ECG painful or dangerous?
A: No. The test is non-invasive and completely safe. It involves placing electrodes on your skin to record your heart’s electrical signals.
Q2: How long does the test take?
A: The actual recording takes only a few minutes. Including setup, the entire process usually takes 10–15 minutes.
Q3: Can ECG results be inaccurate?
A: An ECG provides a snapshot of your heart at a specific moment. Some rhythm issues come and go, so your doctor may recommend additional monitoring if needed.
Q4: Do I need to fast or stop medication before the test?
A: No special preparation is usually required. However, always follow your doctor’s instructions if part of a larger cardiac assessment.
Q5: Can an ECG detect all heart problems?
A: While it’s a valuable tool, some conditions (like early coronary artery disease) may not show up on an ECG. Additional tests such as echocardiography or stress testing may be needed based on your symptoms.
Understand Your Heart, One Beat at a Time
Whether you’re experiencing symptoms or simply checking in on your heart health, a 12-lead ECG is a fast and reliable starting point. It can uncover a wide range of issues –some of which may not show symptoms right away.
At Heart Matters Cardiac Centre, we provide ECG testing as part of our comprehensive cardiac evaluation. Our team is here to guide you through what to expect and what to do next.